Tuesday, November 25, 2025
Investing in Gold: Modern Routes, Returns & Strategies
By Century Financial in 'Blog'

.jpg)
From ancient pharaohs to today’s investors, people have always trusted gold to hold its worth. It’s one of those rare assets that never goes out of style, carrying the weight of history while still powering economies today. It has always been considered a safe-haven asset, protecting wealth during market volatility and periods of inflation.
Investing in gold has its own benefits and risks, so it’s important to align your investment with financial goals and risk appetite. By understanding market trends, taxation rules, and diversification strategies, investors can optimize returns while preserving long-term wealth.
What is Gold Investment & Why It Matters
As a “safe haven” asset, in times of inflation, currency devaluation, or market volatility, gold often retains value better than many other assets. But investing in gold doesn’t only mean buying bars or jewelry. Modern financial markets offer gold as an investment via ETFs, mutual funds, exchange-traded products, and gold funds, each carrying distinct features, pros, and cons.
Unlike stocks or bonds, gold is a tangible asset that isn’t directly tied to corporate earnings or government interest rate policies, making it a strong diversifier for any portfolio. Moreover, the returns on gold over the years have shown resilience compared to many volatile asset classes.
Whether through physical gold, exchange-traded gold instruments, or digital platforms, investors can now access gold in more convenient, secure, and liquid ways. This flexibility makes gold investment not just a wealth-preserving tool but also a strategic component of long-term financial planning.
Key Ways to Invest in Gold
1. Physical Gold
.png)
Gold Bars & Coins
This is the most traditional form of gold investment. It offers tangible ownership, but investors must consider costs like storage, insurance, and purity verification. Liquidity can also be limited compared to the financial instruments and other forms of gold.

Vaulted/Digital Gold
This is a modern alternative where gold is securely stored in professional vaults. Depending on the provider, you may own actual gold (allocated) or simply gain price exposure (unallocated). This removes storage hassles while the price remains linked to physical gold.
2. Gold Mutual Funds
Gold mutual funds are professionally managed funds that invest in a portfolio of gold-related assets. These may include:
Physical gold
Gold mining stocks
A blend of gold-linked instruments
Unlike direct gold investment, these funds allow investors to participate in the gold market without the hassle of storage or high entry costs. They are particularly suitable for those who prefer a systematic investment approach and wish to gain from professional fund management.

Benefits
They offer diversification, expert management, and exposure to gold without the need to store it physically
Managed by experts, making it easier for retail investors to benefit from gold market trends
Can be started with relatively small investments, making them more accessible.
Drawbacks
Fund performance may not exactly mirror gold prices due to management fees and allocation strategies
3. Gold ETFs / Exchange Traded Funds
Gold ETFs (exchange traded funds) are among the most popular modern options. They are listed on stock exchanges and typically backed by physical gold bullion, designed to track spot gold prices.
Pros
High liquidity
Cost-effective compared to owning physical gold
Watch out for
Expense ratios
Whether the ETF is physically backed or synthetic (futures-based)
Tracking errors compared to the commodity’s spot price
.png)
4. Other Gold Funds & Products
Apart from ETFs and mutual funds, investors also have access to a wide range of gold-related products that provide different levels of risk, return, and complexity. These alternatives are often chosen by investors seeking more control, flexibility, or higher potential gains. While they can diversify a portfolio and enhance returns, they also demand a deeper understanding of market dynamics, taxation rules, and associated risks. Selecting the right product depends largely on investment goals, time horizon, and risk appetite.
Gold Exchange-Traded Products (ETPs)
Similar to ETFs but with structural differences that may impact risk, taxation, or liquidity, gold ETPs give you a way to ride gold’s price moves without the hassle of buying and storing the real thing.
Gold Mining Stocks & Funds
Investors can invest in companies that mine and produce gold. While they can offer leveraged exposure to gold prices, these carry additional risks tied to company performance, operational challenges, and geopolitical factors.
Gold Futures & Options
These are derivative contracts that provide leveraged exposure to gold prices. They are highly liquid but involve greater risk, higher margin requirements, and complexity—making them more suitable for experienced traders rather than beginners.
Steps to Invest in Gold via Gold Funds and ETFs
Investing in gold through gold mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded products (ETPs) is convenient and cost-efficient. This eliminates the hassles of storing physical gold. Here’s a quick way you can make better decisions regarding your gold investment:
Step 1 – Define Your Goal & Time Horizon
Before you invest, clarify why you are buying gold:
Wealth preservation

Gold acts as a hedge against inflation and currency depreciation.
Portfolio diversification

Reduces risk by balancing equity or bond-heavy portfolios.
Short-term gains

Short-term trading opportunities during periods of volatility.
Note: Gold tends to shine during risk-off periods, but over short intervals, it may fluctuate significantly. Long-term goals often align better with gold’s stabilizing nature.
Step 2 – Choose the Right Gold Investment Instrument
Different gold investment instruments serve different needs:
Physically-backed Gold ETFs or Funds
These are the best options for investors seeking simplicity and direct exposure to spot gold prices. Ease of investment is also high here.
Gold Mutual Funds
This option offers managed exposure. It is best suited for beginners who prefer expert handling.
Mining Stocks or Sector Funds
This option is quite different from others. It provides potential upside but adds company-specific risks.
Futures & Derivatives:
Derivatives, no matter the underlying, provide heightened exposure, therefore increased risk. It is suitable for experienced traders ready for high volatility and leverage.
Tip: Compare gold mutual funds vs ETFs on aspects like liquidity, fees, ease of trading, and type of exposure.
Step 3 – Research & Compare Before Investing
All investments carry a certain amount of risk. As investors, we are expected to understand and accept the amount of risk we can manage. Doing thorough due diligence is integral before choosing your gold investment vehicle:

Expense Ratio / Management Fees
Lower costs lead to higher net returns.

Underlying Holdings
Check if the product holds physical gold, futures, or mining equities.
.png)
Liquidity
Ensure the fund or ETF has enough trading volume for easy entry and exit.
Tracking Error
Evaluate how closely the ETF or fund follows the gold spot price.

Tax Implications
Understand capital gains tax rules (short-term vs long-term).
Additional Options to Explore
Gold ETFs or ETPs are listed on global exchanges for international exposure.
Commodity trading platforms offering gold as part of their product basket.
CFD Gold Contracts for short-term positions (higher risk).
Always factor in margins, commissions, and platform fees before committing capital.
Step 4 – Execute Your Gold Investment
Once you’ve finalized your instrument, open a trading or investment account with a regulated broker or financial institution. Ensure you use secure, reputable platforms such as the Century Trader App, or equivalent, that provide:
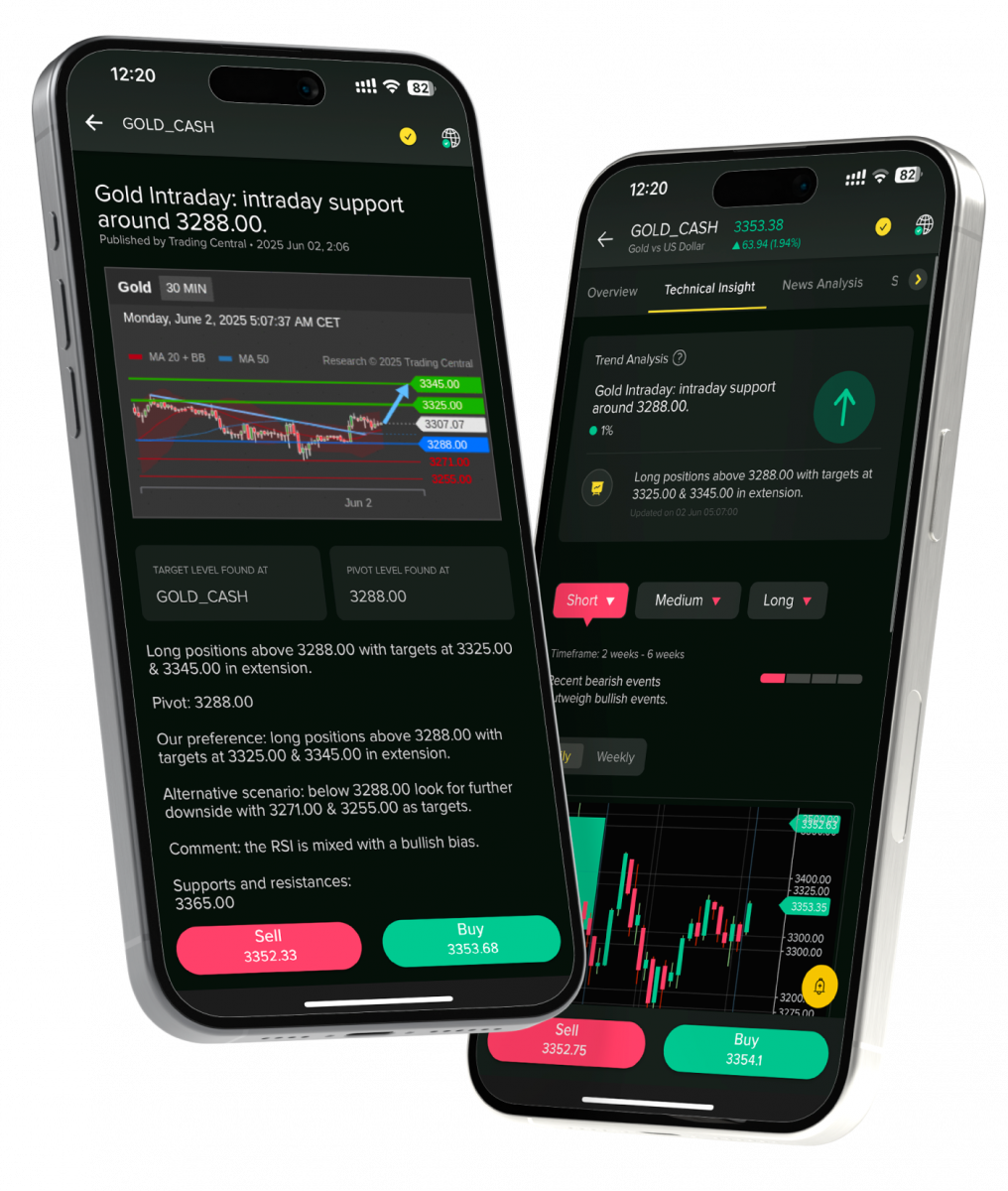
Step 5 – Portfolio Allocation & Risk Management
Returns on Gold & What Drives Them
Understanding what influences gold prices helps investors set realistic expectations and align strategies with their financial goals. Unlike equities, which generate income through dividends or bonds that pay interest, returns from gold are driven mainly by price appreciation and demand-supply dynamics.
Recent Trends
In H1 2025, gold ETFs globally witnessed record inflows as investors turned to gold amid economic uncertainty, currency weakness, and inflationary pressures. This shows how market sentiment often drives demand for gold in volatile times.
Inflation & Monetary Policy
Gold prices typically rise when inflation is high or when currencies weaken, as investors seek safety in hard assets.
Global Demand & Supply
Factors such as central bank gold purchases, jewelry demand in emerging markets, and mining output significantly impact gold’s price dynamics.
Interest Rates
Lower real interest rates typically boost gold’s appeal, as the opportunity cost of holding a non-yielding asset declines.
Currency Movements
Since gold is priced in U.S. dollars, fluctuations in USD value directly affect gold returns globally. A weaker dollar generally boosts gold prices.
Risks & Volatility
While gold is considered a safe-haven asset, it does not generate interest or dividend income. Its price can be volatile, often influenced by geopolitical tensions, speculative trading, and unexpected macroeconomic events.
Gold vs Other Assets: Mutual Funds, Stocks, etc.
Diversification is the mantra every investment portfolio is built on. It is not limited to shares of different companies, but investments in different asset classes.
When building a diversified portfolio, it’s essential to compare how gold performs alongside traditional investment asset classes such as equities, mutual funds, and bonds. Each asset class has unique characteristics, risks, and benefits.
Gold stands out as a non-yielding but protective asset, while equities and mutual funds are designed for growth and income generation. Here’s a snapshot of some of the key differences:
| Comparison Aspect | Gold / Gold ETFs & Funds | Equities / Stocks / Mutual Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Income / Dividends | None | Yes, via dividends |
| Liquidity | Very liquid (especially ETFs) | Usually liquid, but it depends on the market/stock |
| Volatility correlation | Low‐to‐negative correlation with stock markets at times | Often high correlation with the market cycle |
| Cost of ownership | Fees, storage (if physical), custody costs; ETFs have lower costs | Brokerage fees, fund fees, and sometimes performance fees |
| Inflation protection | Stronger | Mixed; equities may lag or lead depending on the environment |
Tips to Maximise ROI & Minimise Risk
Gold investment can be rewarding, but like any asset, it comes with risks. By following some proven strategies, investors can enhance returns while reducing exposure to market volatility. The key lies in disciplined investing, diversification, and monitoring economic trends that influence gold prices.
Start Small & Scale Up
Especially if you are new to gold investment, begin with small amounts to understand market behavior. Once comfortable, you can gradually increase your exposure.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Instead of investing a lump sum, buy gold periodically (monthly or quarterly). This strategy helps smooth out price fluctuations and reduces the risk of buying at peak levels.
Avoid Paying High Premiums
When buying physical gold, be mindful of premiums added over the market price. Opt for reputable dealers and compare rates before purchasing.
Watch Fees & Costs
Hidden costs can erode returns. Pay attention to expense ratios in gold ETFs, brokerage charges, storage fees for physical gold, and bid-ask spreads.
Track Macro-Economic Trends
Gold prices are highly influenced by inflation, interest rates, central bank policies, and geopolitical tensions. Staying up to date on these factors can help you make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Gold remains a compelling component in a diversified investment portfolio. Whether through gold mutual funds, gold ETFs (exchange-traded funds), sovereign gold bonds, or other structured products, it serves as both a hedge against inflation and a store of value.
By adding gold to your investment strategy, you can balance risk, preserve wealth during uncertain times, and potentially improve long-term returns. The key lies in choosing the right investment vehicle, monitoring costs, and staying informed about macroeconomic factors that influence gold prices.
FAQs
1- What is the difference between a gold ETF and a gold mutual fund?
A: Gold ETFs can be traded on exchanges like a stock and often track the spot price of gold. A gold mutual fund may hold gold-related assets (bars, mining stocks) and is managed actively.
2- Are gold ETFs physically backed or based on derivatives?
A: Some gold ETFs are physically backed (they actually hold gold in vaults), while others replicate gold exposure via futures, synthetic instruments, or other derivatives.
3- What returns can I expect from gold investments?
A: Returns vary with economic cycles. Historically, gold has delivered moderate returns over long periods, often swinging significantly in shorter time frames.
4- How much of my portfolio should be allocated to gold?
A: It depends entirely on your risk tolerance. Equity and gold have opposing cycles, making gold a good hedge against your overall stock portfolio risk.
5- What are the costs and risks associated with investing in gold ETFs/funds?
A: Gold is not a one-stop solution to all your investment woes. There are costs and potential downsides while trading or investing in gold funds.
Costs include management and expense ratios, bid-ask spreads, brokerage fees, possible currency conversion fees, and, in some cases, storage/custody fees (if physical backing). Risks include price volatility, currency fluctuations, counterparty risk (for synthetic products), regulatory risk, and opportunity cost (money tied up in gold may miss returns elsewhere).
Related Reads
This marketing and educational content has been created by Century Financial Consultancy LLC (“Century”) for general information only. It does not constitute investment, legal, tax, or other professional advice, nor does it constitute a recommendation, offer, or solicitation to buy or sell any financial instrument. The material does not take into account your investment objectives, financial situation, or particular needs.
The opinions expressed by the hosts, speakers, or guests are their own and may change without notice. Information is based on sources we consider to be reliable; however, Century does not guarantee its accuracy, completeness, or timeliness and accepts no liability for any loss arising from reliance on this content.
Trading and investing involve significant risk, and losses may exceed initial deposits. Past performance is not indicative of future results. CFDs and other leveraged products are complex instruments that may not be suitable for all investors. Please ensure you understand how these products work, the associated risks, and seek independent professional advice if necessary.
Century is licensed and regulated by the UAE Capital Market Authority (CMA) under License Nos. 20200000028 and 301044.
Please refer to the full risk disclosure mentioned on our website.









.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


